Deep Quantum Monte Carlo
Insert image
Insert image left
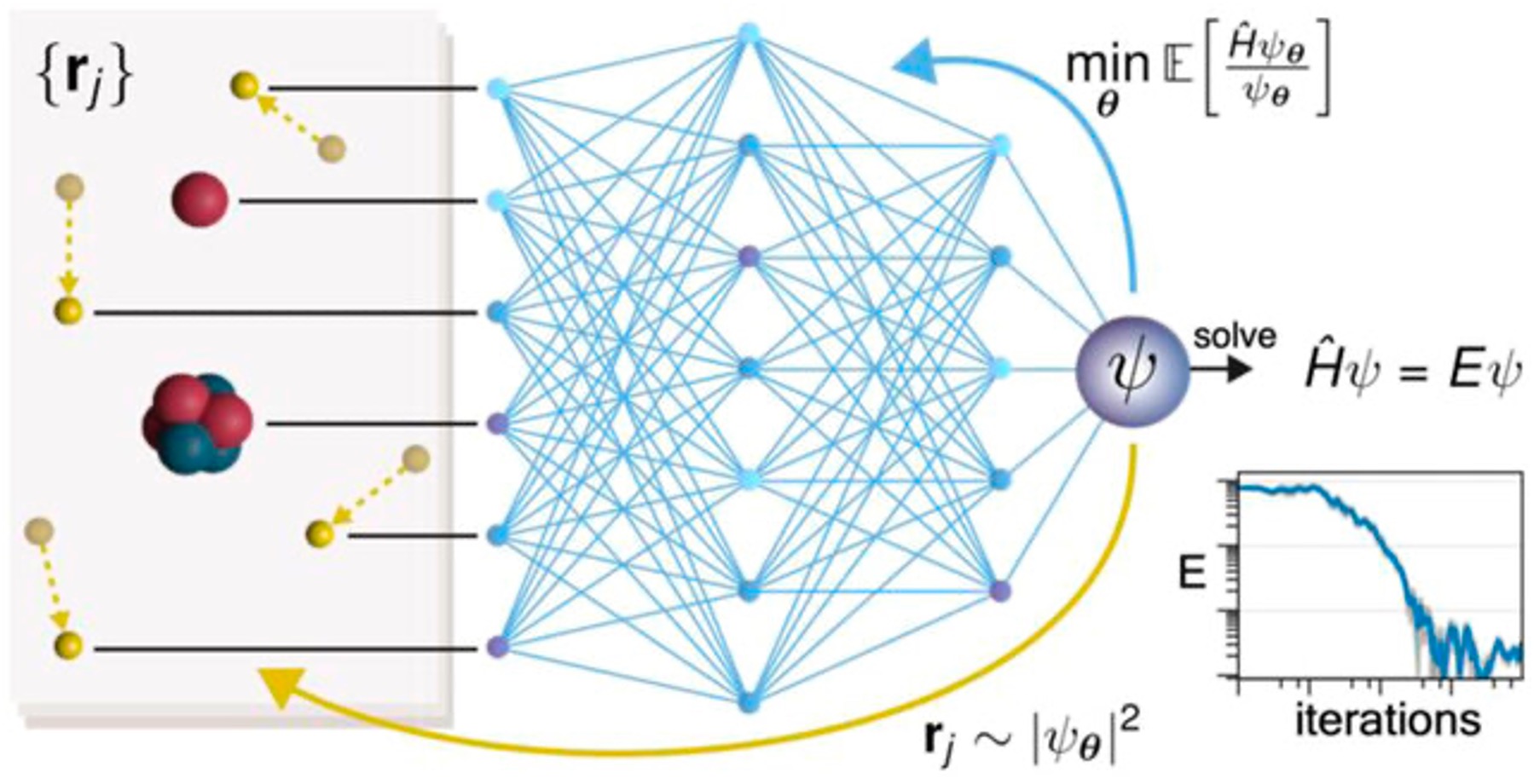
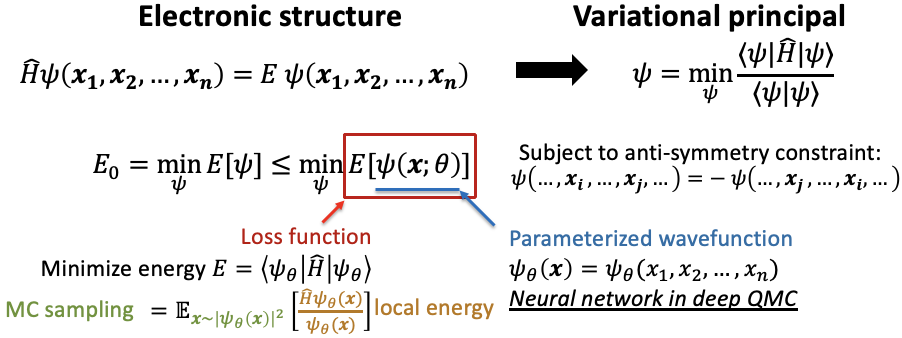
Deep Quantum Monte Carlo (deep QMC) is a cutting-edge approach that combines deep learning with variational quantum Monte Carlo (VMC) methods to directly solve the electronic Schrödinger equation for molecules and materials. By using neural networks to approximate wavefunctions, deep QMC can achieve wavefunction-level accuracy while handling complex, strongly correlated systems that are typically challenging for traditional quantum chemistry methods.
Current active community repo: Deep QMC repo by FU Berlin team
Suggested reading: Review paper by Hermann et al 2023; Excited state deep QMC paper by Pfau et al 2024
🧪 General formualtion & Status of Deep QMC:
✅ Many good results on both ground state & excited state problems
🚧 Problem 1. Still expensive: Need to further speed-up DeepQMC
🚧 Problem 2. Usually only get energies: WF can provide more properties
🧠 Our Efforts:
Right: electron wandering during traininng for LiH, credit to Zeno Schatzle
Solution 1: A pretrained wavefunctioin fundation model & its finetuning for downstream applications
- Orbformer : An ab initio wavefunction foundation model for ground state molecular systems.
Solution 2: Properties extraction for DeepQMC:
- Neural electron real-space density (NERD) : A neural electron real-space density model based on DeepQMC wavefunctions, enabling accurate, basis-set-free electron density predictions for evaluating density-based molecular properties.
AI x Quantum Computing for Quantum Chemistry
AI for Quantum Computing in NISQ Era
We focus to use AI to to enhance the design and execution of quantum algorithms on Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) hardware. Specifically, our research explores how AI can be applied to:
🧩 Design more hardware-efficient ansatzes and quantum circuits;
🛡️ Enhance error resilience and correction strategies;
⚙️ Improve circuit parameter optimization in the presence of quantum noise.
Our goal is to build smarter, more robust quantum workflows that unlock the potential of near-term quantum devices for scientific discovery.
- DARBO (Double Adaptive-Region Bayesian Optimization): AI powered efficient optimizer for quantum circuits on real quantum hardware (over 1000x cost reduction).
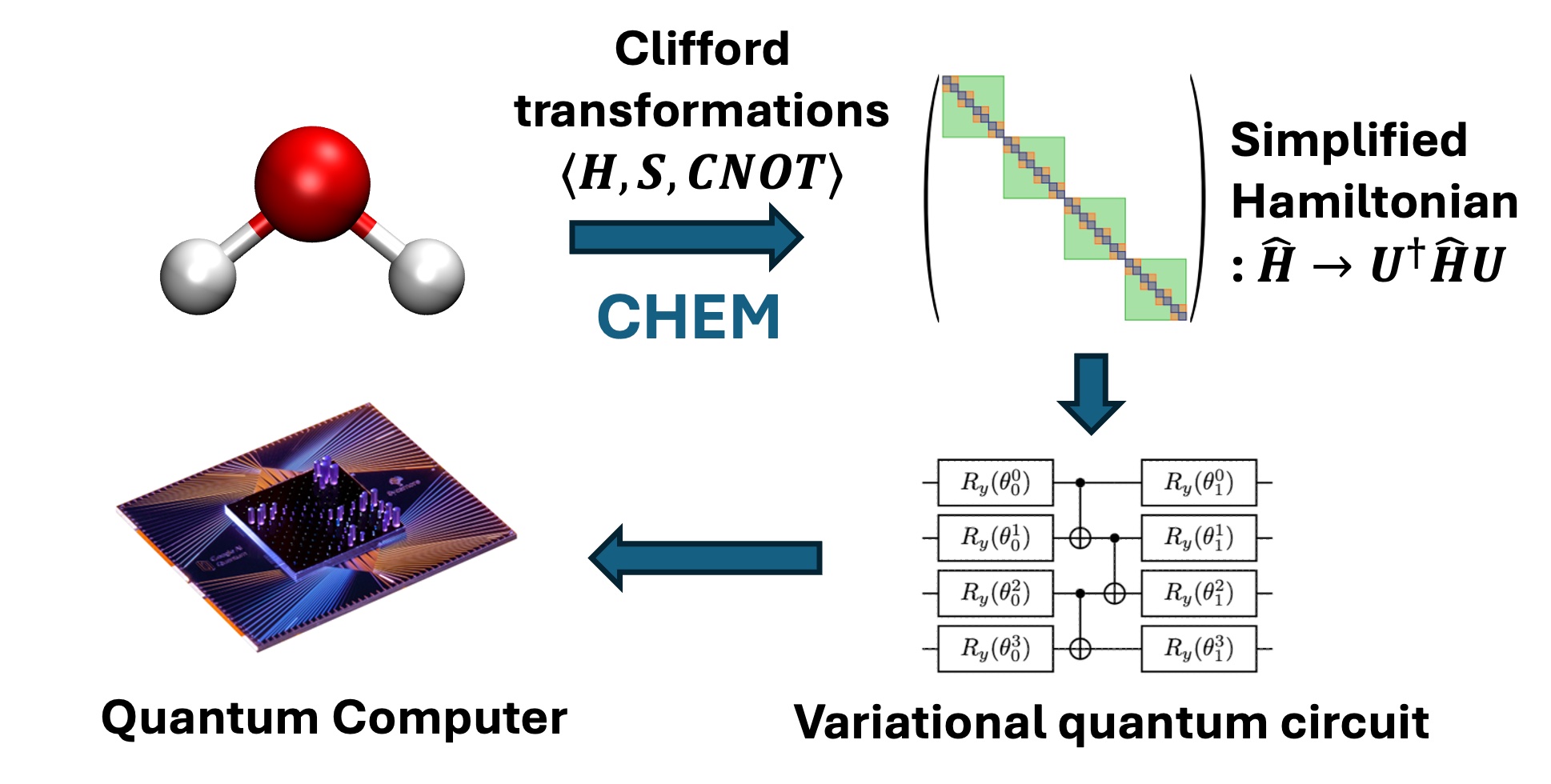
Hardware Efficient Ansatz (HEA) for Quantum Chemistry via Quantum-classical Hybrid Approach
Our goal is to fully harness the power of quantum algorithms by “letting quantum algorithms handle quantum problems” in chemistry. We focus on hybrid quantum–classical methods to design more efficient ansatzes and computational protocols for solving electronic structure problems on near-term quantum devices.
- CHEM (Clifford Hamiltonian Engineering for Molecules): a hybrid quantum–classical method that applies Clifford transformations to molecular Hamiltonians, enabling more accurate and hardware-efficient quantum chemistry simulations on NISQ devices.